Breast cancer is a malignant tumor of the breast. The term ‘cancer’ refers to a group of several related diseases that usually develops due to uncontrollable cell division. These cells are called cancer cells.
Cell is a basic unit of life and all parts of your body are made up of cells that usually divide to generate even more cells whenever your body needs.
Breast cancer is one of the most frequent types of cancer among women. In the United States, about 220,000 women are developing breast cancer yearly.
Breast cancer can be described in four different stages. The cancer cells in the breast can spread outside the breast to underarm lymph nodes to the bones, brain, liver, or lungs (where cells usually grow and multiply) through bloodstream or lymph system.
This stage of breast cancer is known as metastatic breast cancer and the tumors that form in the organs and tissues are called metastases.
In other words, metastatic breast cancer refers to a breast cancer stage that spreads within or beyond the breast and lymph nodes to other parts of the body. It is also known as stage IV breast cancer, an advanced stage of breast cancer.
Remember that metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer stage although it is not found in the breast.
The metastatic breast cancer symptoms depend up on the location of the metastases and the extent of the cancer spread. The symptoms of metastases breast cancer are as follows:
Lump may form in the breast, chest or under the arm if the cancer is in the breast or near the chest wall. You will also notice a change in the size, shape and skin of the breast. There will be pain in the chest wall and/or discharge from the breast.
Bone metastases generally cause bone pain, fractures, fatigue, constipation and spinal cord inflexibility. Metastases in the lung usually lead to shortness of breath, cough, too much fatigue, and pain in chest wall.
Nausea, lack of appetite, weight loss, high abdominal girth, and skin itching are caused by liver metastases.
The brain metastases are accompanied by loss of memory, confusion, unclear vision, inability to speak and to listen, neurological pain, unable to stand or walk, weakness, and headaches.
It is important to remember that developing any of these symptoms doesn’t always indicate that you are with metastatic breast cancer. So, consult your doctor right away for treatment if you exhibit metastatic breast cancer symptoms.
The metastatic breast cancer treatment is based on the factors such as tumor symptoms, location, size, and its extent. It also depends on your general health condition, tolerance to medications and personal preference.
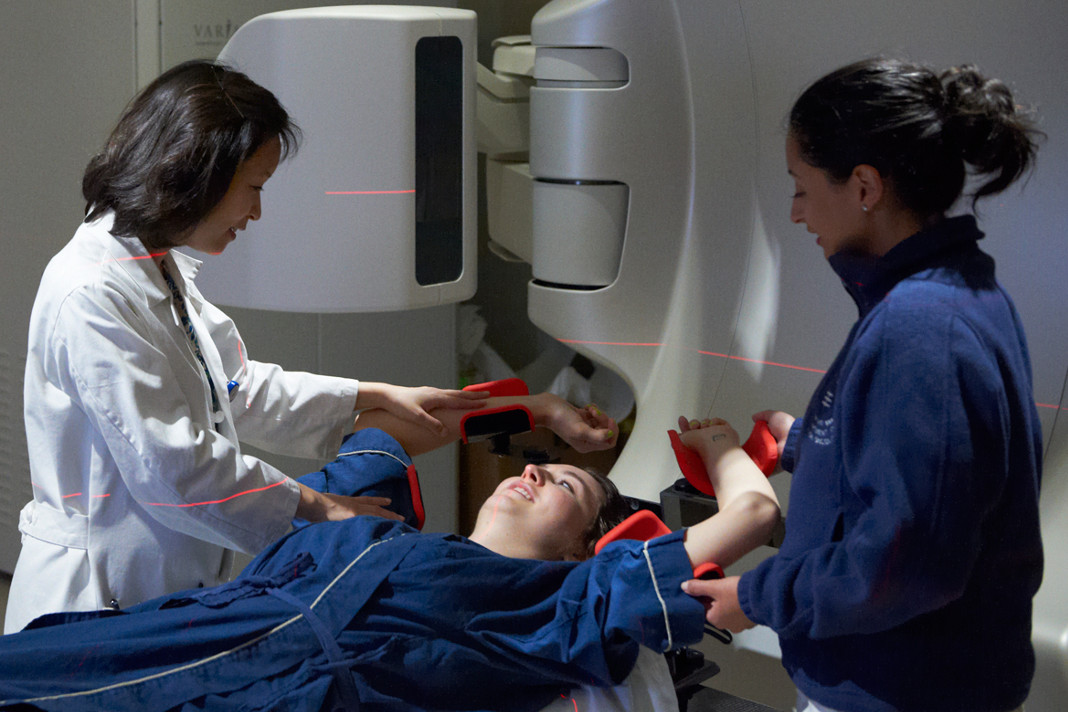
The most common treatments for metastatic breast cancer include hormone replacement therapy, chemotherapy, biophosphonates, radiation therapy and surgery. However, these treatment options will be used either alone or in combination.
It is to be noted that these treatment options cannot cure metastatic breast cancer, but can decelerate the cell division and lessen or eliminate symptoms.